Exploring the Intricate World of Electrical Cables From Construction to Applications in Modern Technology
 Jun 27,2025
Jun 27,2025
 Suke
Suke
Electric cables, unheralded heroes of the modern age, quietly conducting the energy and information that underpin our world. Whether it’s the complex circuitry of our smartphones or the massive networks below ground that illuminate cities, they are the crucial building blocks of our modern world. And yet, they are those elements that are most likely to escape attention.
The Anatomy of Electrical Cables
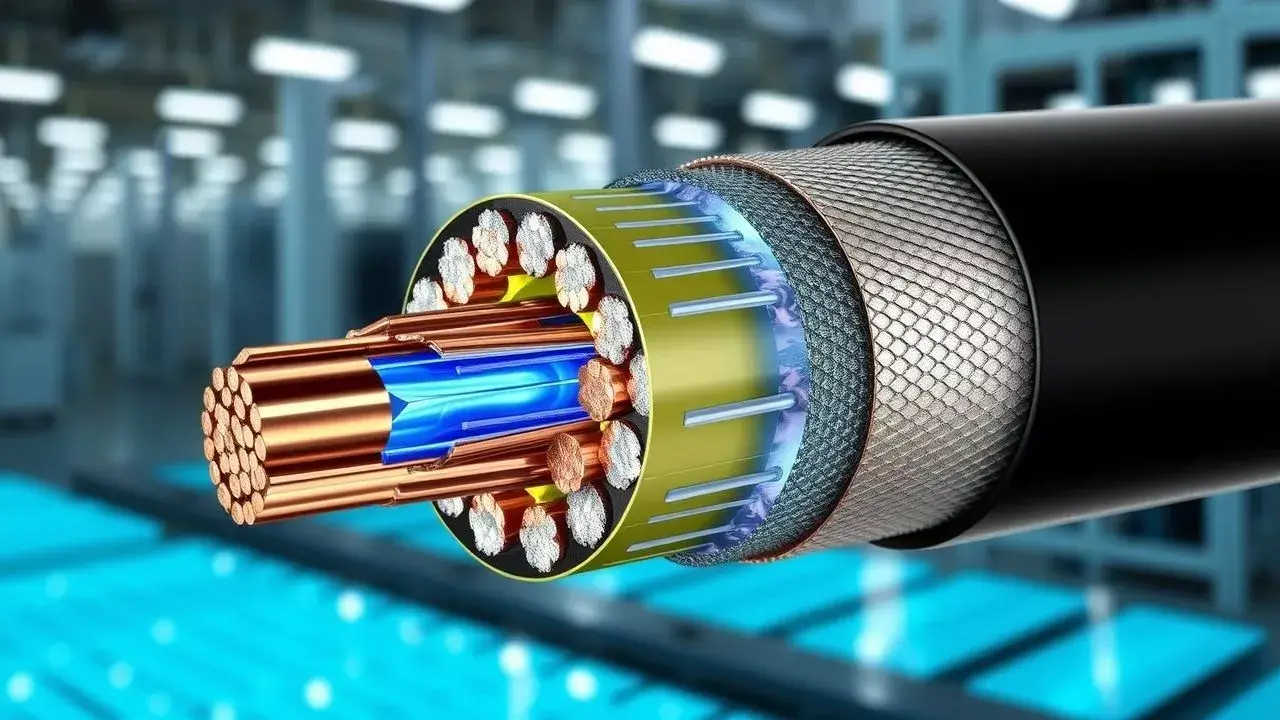
The average power cord may appear to be a straightforward collection of wires at first glance, but its design is far from simple. Providing support and structure to any cable is its central component, the conductor, which, for the most part, is made from either aluminium or copper, in large part thanks to their good conductivity. These conductors may be solid or stranded; with the stranded wire having a thicker exterior insulating jacket, due to the use of stranded conductors (giving better flexibility and durability). An insulation, that is insulation layer, surrounds the conductor to insulate the conductor from electrical leakage and from the environment such as moisture, heat, and the like. In addition to insulation, however, many cables are also covered by extra layers for additional protection. A protective cover, often braid or foil, serves to protect the data cable against electromagnetic interference for stable signal transfer. The jacket's outer layer offers excellent cut and laceration protection, abrasion resistance, as well as resistance to gas and vapor permeation. Beautiful, well-designed layered structure cables can provide extra strength to the cables so they won’t get damaged from daily pursuits, such as buried in the ground or water, and endure stress from third party via human movement.
Kinds of Electrical Cables and Their Uses
There’s an enormous range of electrical cables available, and each one is designed for a purpose. Power wires, for example, are engineered for carrying high-voltage electricity for a long time. “We use those a lot in power grids, in industrial machinery, and in household wiring.” They have a very rugged design and so very low loss of energy and maximum safety, even under heavy load.
Pulled lines, busy crossbar, Ethernet, and even fiber optic cables, on the other hand, are designed for speed and accuracy. These are fiber optic cables, which use light to transfer data, and they are changing the world of communication and data because of their incredible bandwidth and speed. Another type, coaxial cables, is known for its reliability in the television and internet world, providing reliable signal transmission with minimal interference. Every type of wire has a specific purpose, illustrating the diverse flexibility of this critical equipment.
The Cabling that is Used in FoIP Technology
Today in our interconnected world you can find electrical cables at the heart of so many technologies. Smartphones, laptops and other electronic devices inside the wiring are intricate. Charging cables, those oft-overlooked wonders of engineering that bring power and data simultaneously. Without these, none of those modern conveniences about which we’re so crazy would be possible.
On a vaster scale, cables make possible the infrastructure that gives cities their power and links continents together. Take submarine cables, which stretch across ocean beds to connect worldwide communication systems; that provides for immediate communication and data sharing around the world. Cables link solar panels and windmills to the grid in renewable power systems, enabling clean energy to be generated efficiently. The presence of cables, along with their intersection with technology, serves as a reminder of the irreplaceable aspect of these objects in creating the world as we know it today.
Innovations and Future Trends
The electrical cable world doesn’t stand still, on the contrary, it changes with the technological development. One interesting development is the EMA’s emerging superconducting cables that can move electricity with no resistance, creating a near-lossless experience of efficiency. In the future, these cables may become a practical tool as further development seeks to eliminate the requirement of extreme cooling.
Another development is the incorporation of intelligent functions in cables. For example, modern cables can track their own health, sensing fatigue and potential failure well in advance of catastrophic breakdowns. Such an aggressive strategy adds a safety margin and minimizes maintenance expenses. Furthermore, the demand for sustainability is also influencing the upswing in eco-friendly cords that are made of recyclable materials, along with attempts to create a more eco-friendlier planet.

Challenges and Considerations
There are, however, a number of problems encountered with electrical cables despite their many advantages. One significant problem is cooling as in high power use. High temperatures can cause deterioration of insulation and shorten cable life, therefore, advanced cooling is required. There's also the question of the environmental cost of manufacturing and discarding cables. There are risks in the ecological damage heavy metals and plastics used in cables might cause, so the industry is looking for greener alternatives.
Furthermore, the demand for faster and more reliable data transmission is also stretching cables to its max. Engineers constantly twist and tweak and create to meet these needs, performing a dance based on performance, cost and durability. The new generation of cables of tomorrow As technology evolves, tomorrow's cables will have to be even more resilient, efficient and versatile to keep up with the rapidly changing environment of modern technology.

 Home
Home Shipboard Wire Market Trend Analysis: Global Demand Growth and Selection Guide to 2025
Shipboard Wire Market Trend Analysis: Global Demand Growth and Selection Guide to 2025  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address